This story is a part of PostgreSQL Table Partition. The story tells more information about range partition with example. Range partition is kind of a horizontal partition.
Let’s assume there is a service called promotions. Entity of this promotions service is promotion. Any given time huge amount of marketing promotions are insert into promotion table. Once published promotion records/ events, those records are no longer required to store in the table. But just in case these published data will keep for a month and then delete them.
This kind of a situation, ideal way to remove stale data from the table is either delete the record from table or use range partition to delete them. Bulk deletion from the table isn’t a good solution. As this service process a lot of records any given time. So, bulk deletion will impact to the database operations. In other words it will impact to the performance of the database.
Range partition is a good solution for this kind of situation. Data deletion can be done by dropping the partition as it much faster and lower impact to the database operations.
Following example shows how to use range partitions to perform bulk deletion.
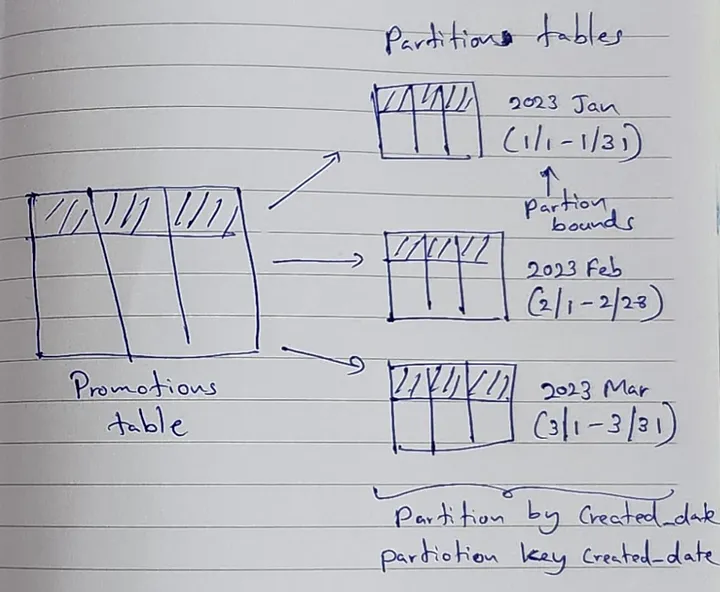
Partition key — Determines which partition is used for data.
Partition bounds — Range or minimum and maximum values in a partition.
Constraints — Each partition has its own indexes and constraints.
-- Table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS promotions
(
id uuid NOT NULL,
category VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
created_date date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT promotions_pkey PRIMARY KEY (id, created_date)
) PARTITION BY RANGE (created_date);
-- Partitions
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS promotions_default PARTITION OF promotions
DEFAULT;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS promotions_y2023m01 PARTITION OF promotions
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-01-01') TO ('2023-01-31');
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS promotions_y2023m02 PARTITION OF promotions
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-02-01') TO ('2023-02-28');
After executing the above statements, you can see how tables are created in PGAdmin console.
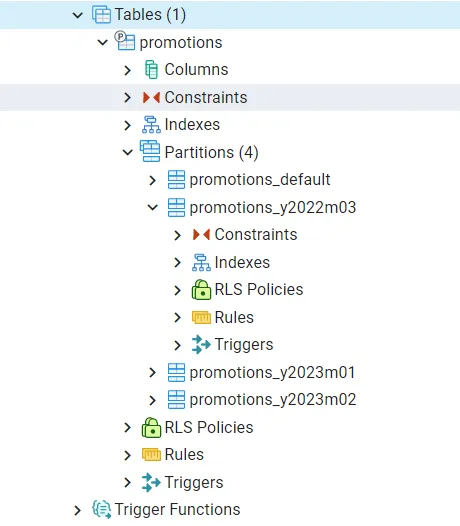
Let’s insert some records and see how records will be organize in partitions. That is it for now. Thanks for following the article.