Before we start to build the API, let’s discuss about Spring WebFlux and its architecture.
Spring WebFlux is a reactive web framework introduced in Spring 5 that allows developers to build asynchronous, non-blocking web applications using the Reactive Streams API. Unlike the traditional Spring MVC framework, which is based on the Servlet API, Spring WebFlux is based on the reactive foundation provided by the Reactor project.
WebFlux is particularly useful for building high-performance, scalable, and resilient web applications that can handle a large number of concurrent connections. It’s also well-suited for building microservices, APIs, and real-time applications that require low latency and high throughput.
The Reactor Core is responsible for providing the reactive programming foundation and includes the following components:
-
Flux: A stream of data that can emit zero or more items
-
Mono: A stream of data that can emit zero or one item
-
Scheduler: A mechanism for scheduling and executing asynchronous tasks
The Reactor Netty is a non-blocking I/O framework that provides a high-performance and scalable web server for Spring WebFlux applications. It includes the following components:
-
HttpServer: A web server that listens for incoming HTTP requests
-
HttpClient: A client for making HTTP requests to other servers
-
TcpServer: A server for handling TCP connections
-
TcpClient: A client for establishing TCP connections to other servers
-
WebHandler: A handler for processing incoming HTTP requests and generating HTTP responses
-
RouterFunction: A functional programming model for defining routes and handling requests
-
HandlerFilterFunction: A filter for modifying or intercepting incoming HTTP requests and outgoing HTTP responses
-
WebClient: A reactive client for making HTTP requests to other servers
Request Processing in Spring WebFlux
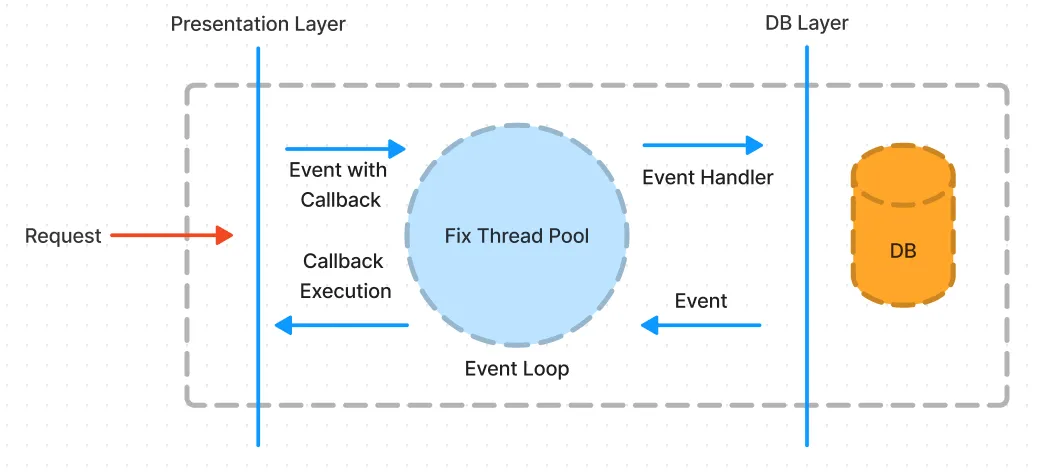
The processing of a request is based on an event loop model. The event loop is a single-threaded loop that is responsible for handling all incoming requests and responses.
When a request is received, it is added to a queue and the event loop picks it up and starts processing it. The event loop uses non-blocking I/O to communicate with external systems, such as a database or external API, which allows it to handle many requests simultaneously.
During the processing of a request, the event loop does not block and waits for external resources to become available. Instead, it continues to process other requests in the queue until the external resource becomes available. This is achieved through the use of reactive programming constructs such as Flux and Mono.
Once the external resource becomes available, the event loop picks up the request from the queue and continues processing it. Once the processing is complete, the event loop sends the response back to the client and moves on to the next request in the queue.
The use of an event loop allows Spring WebFlux to handle large volumes of requests efficiently and with low latency, making it a popular choice for building high-performance web applications. Additionally, the non-blocking nature of the event loop allows for efficient use of server resources, which can reduce costs and improve scalability.
Now that we have discussed about Spring WebFlux, let’s create an API to gain a deeper understanding of how it works in practice. By building an API, we can explore the various components of Spring WebFlux in more detail.
Create a new Spring Boot project with the Reactive Web dependency using the Spring Initializr.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
@EnableWebFlux is a Spring annotation that enables the WebFlux framework in a Spring Boot application. This annotation is usually added to the main application class to enable the use of reactive programming in the application.
@WebFluxTest is a Spring Boot test annotation used to test WebFlux controllers in a Spring Boot application. This annotation enables the auto-configuration of the WebFlux infrastructure and sets up the necessary components for testing WebFlux controllers. When @WebFluxTest is used, it creates a test context with a minimal configuration and starts an embedded server that listens on a random port for HTTP requests.
WebTestClient is a class provided by Spring Framework’s spring-webflux module that allows you to test and interact with reactive web endpoints in a Spring Boot application.
Sample demo application available here.
Thank you for your interest.